Kubernetes - Use Monopam to Configure Secret Store
This document will help you to configure Kubernetes to use Monopam Vault for Secret Storage. Before you continue, you need to make sure you have a valid license and configuration on your Monopam.
Monopam uses External Secrets Operator (ESO) to bind Monopam credentials to Kubernetes.
To configure your Monopam Vault to use in Kubernetes, follow the instructions.
📘 Instructions
This documentation will contain 5 steps for integration.
Install External Secrets Operator (ESO) to Kubernetes
Create Monopam Access Key
Add Monopam Access Key to Secret Storage
Configure External Secrets Operator in Kubernetes
Map your Monopam Vault Item (Credential) to the Kubernetes
Read Secret Text
Read UserName and Password
Test Vault with Example Deployment
Highlight important information in a panel like this one. To edit this panel's color or style, select one of the options in the menu.
1. Install External Secrets Operator (ESO) to Kubernetes
You can follow the installation document of External Secrets Operator.
If you already have External Secrets Operator, you can skip this step.
🖥️ External Secrets Operator - Getting Started
2. Create Monopam Access Key
To access vault items from Monopam API, you need to create an Access Key in Monopam. You can follow the instructions.
Sign in to your Monopam Environment.
Go to the Access Keys
Add New
Give your Access Key a Name
Copy you Access Key (We are gonna use it on Kubernetes)
Click OK
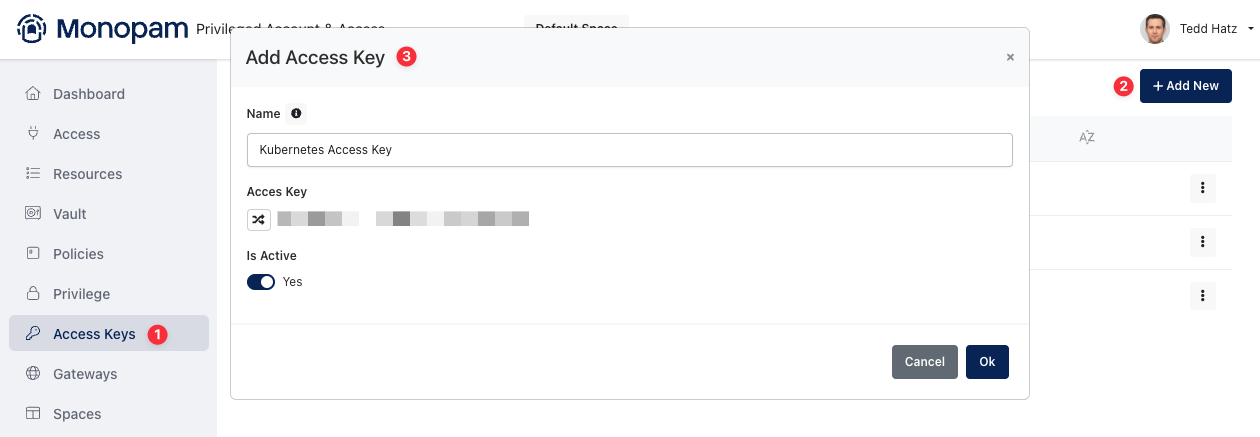
You have successfully created your Access Key.
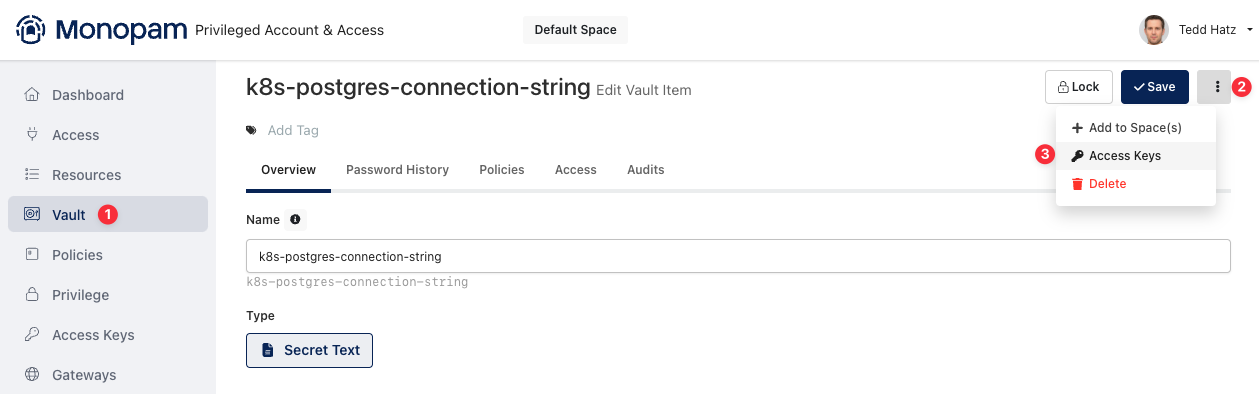
If you want to allow this access key to read a vault item, you need to add that vault item to the Access Key.
Click the Vault
Go to the your Vault Item
Click the “:” button on the top of the right
Select your Access Key on the list and Click OK.
3. Add Monopam Access Key to Secret Storage
Now we need to store Monopam Access Key in Kubernetes Secret Storage.
Namespace Information
After you installing External Secrets Operator, it will also create a namespace external-sercrets. All our deployment of this dependency will be there. If you want custom namespace for your secrets and dependency, you may need configure your namespace definitions.
Use the following deployment file to create Monopam Access Key in Kubernetes
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: monopam-vault-access-key
namespace: external-secrets
stringData:
apikey: "XXXXXX-YYYYYY-ZZZZ-AAAA-TTTTTTTTT" # Your Monopam Vault Access Key4. Configure External Secrets Operator in Kubernetes
Deploy following YAML file in your Kubernetes.
Before doing this change the <MONOPAM-URL> with your instance URL.
apiVersion: external-secrets.io/v1beta1
kind: ClusterSecretStore
metadata:
name: monopam-vault-store
namespace: external-secrets
spec:
provider:
webhook:
url: "https://<MONOPAM-URL>/api/v1/vault/{{ .remoteRef.key }}"
result:
jsonPath: "$.data.{{ .remoteRef.property }}"
headers:
Content-Type: application/json
MonoPam-Vault-Access-Key: "{{ print .auth.apikey }}"
secrets:
- name: auth
secretRef:
name: monopam-vault-access-key
namespace: external-secrets # Only used in ClusterSecretStores5. Map your Monopam Vault Item (Credential) to the Kubernetes
Deploy the following YAML file. Before doing it change the following parameters.
Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| This is your Kubernetes Secret name to put secret/username/password in. |
| This is your Monopam Vault Item Name to read from. |
| Which parameter do you want to bind on Kubernetes. |
| Which property do you want to read from Monopam Vault of the Vault Item / Credential. |
| Which namespace Secret should be mapped / created. |
refreshInterval | RefreshInterval is the amount of time before the values reading again from the SecretStore provider Valid time units are "ns", "us" (or "µs"), "ms", "s", "m", "h" (from time.ParseDuration) May be set to zero to fetch and create it once 15s means, Kubernetes will fetch the credential from Monopam’s Vault every 15s. |
Read - SecretText
apiVersion: external-secrets.io/v1beta1
kind: ExternalSecret
metadata:
name: <TARGET-SECRET-NAME-ON-K8S>
namespace: <TARGET-NAMESPACE>
spec:
refreshInterval: "15s"
secretStoreRef:
name: monopam-vault-access
kind: ClusterSecretStore
target:
name: <TARGET-SECRET-NAME-ON-K8S>
data:
- secretKey: SecretText
remoteRef:
key: "<VAULT-ITEM-NAME-OR-ID-ON-MONOPAM>"
property: <WHICH-PROPERTY-TO-READ>Read - UserName and Password
apiVersion: external-secrets.io/v1beta1
kind: ExternalSecret
metadata:
name: <TARGET-SECRET-NAME-ON-K8S>
namespace: <TARGET-NAMESPACE>
spec:
refreshInterval: "15s"
secretStoreRef:
name: monopam-vault-access
kind: ClusterSecretStore
target:
name: <TARGET-SECRET-NAME-ON-K8S>
data:
- secretKey: username
remoteRef:
key: "<VAULT-ITEM-NAME-OR-ID-ON-MONOPAM>"
property: UserName
- secretKey: password
remoteRef:
key: "<VAULT-ITEM-NAME-OR-ID-ON-MONOPAM>"
property: Password6. Test Vault with Example Deployment
This deployment is used to verify whether the password or secrets obtained through Monopam are applied to the pod as an environment or not.
#This is a example deployment for Kubernetes to test Monopam Vault items.
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
labels:
app: monofor-test
name: monofor-test
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: monofor-test
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: monofor-test
spec:
hostname: monofor-test
restartPolicy: Always
containers:
- image: nginx
name: monofor-test
resources:
requests:
cpu: 100m
memory: 128Mi
limits:
cpu: 250m
memory: 256Mi
env:
# This env for user-pass
- name: TEST_USERNAME
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: monopam-test-user-pass
key: username
- name: TEST_PASSWORD
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: monopam-test-user-pass
key: password
# This is for secretText
- name: TEST_SECRET
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: monopam-test-secret
key: SecretTextCopy and save below example as a monofor-test.yaml
Deploy with kubectl apply -f monofor-test.yaml
Then check pod is working or not
kubectl get pods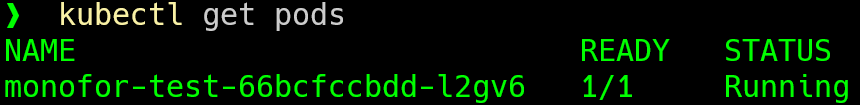
Now you can verify environment which is obtained from secrets.
kubectl exec -it monofor-test-66bcfccbdd-l2gv6 -- /bin/sh -c 'env | grep TEST_'
It can be delete test deployment with below command
kubectl delete -f monofor-test.yamlFinish
This will help you to create and map Kubernetes Secrets from Monopam.
Knowledge Base
Vault Item Types for Read Vault Item
Vault Item Type | Properties |
|---|---|
UserName and Password |
|
PKI |
|
Secret Text |
|
OTP |
|
